Overview of WSO2 MB 3.0.0 DBMS Support
There are lot of architectural changes in WSO2 Message Broker (MB) 3.0.0. We can fairly say its totally different in terms of the architecture compared to WSO2 MB 2.2.0. All these changes were done to improve performance and give more flexibility to the end user.
One of the key features that’s introduced with MB 3.0.0 is its RDBMS support. Previously it was all about Cassandra. Whether you like it or not If you are using MB you had to stick with Cassandra. With MB 3.0.0 you can connect MB to either Cassandra (Either with Hector or CQL), MySQL, MS-SQL, Oracle, PostgresSQL or H2 data store.
Design
In MB, core functionality is handled by Andes. Andes is protocol independent and is cluster aware. MQTT and AMQP protocol implementations talks to Andes to get its work done. Andes mainly uses two data stores for data persistence. They are AndesContextStore and MessageStore.
Note:
- MessageStore is an interface in MB. All messages related persistence tasks (message storing/retrival/deletion) are handled by classes implementing this interface.
- AndesContextStore is an interface in MB. Tasks that are not directly related to messages (create/retrieve/delete queues, exchanges etc) but need to be persisted are handled by classes implementing this interface.
By way of AndesContextStore and MessageStore interfaces, in MB 3.0.0, tight coupling between specific Database Management System (DBMS) and Andes is removed. Therefore supporting a new DBMS is a matter of implementing a class with specific DBMS related implementation and configuring MB to use that implementation at start-up.
Following is the class diagram of MB 3.0.0 that comes with specific implementation for several DBMS types
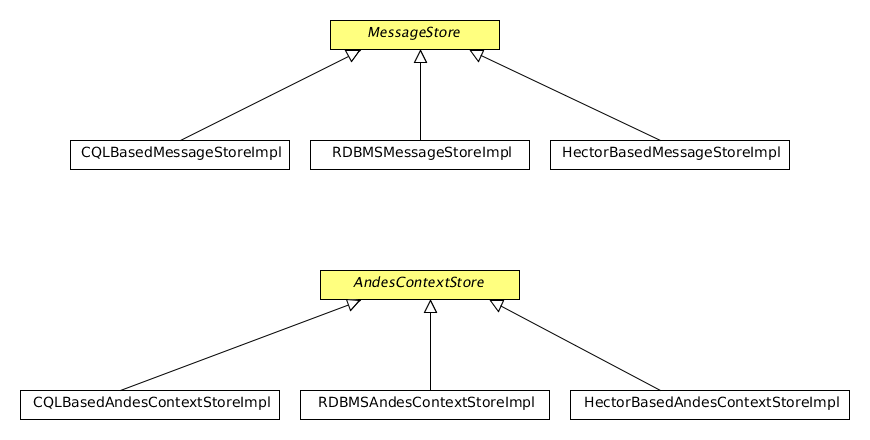
RDBMS related implementations are written using ANSI SQL so that it can be used with many RDBMS’s. This includes MS-SQL, Oracle, MySQL, PostgresSQL, H2.
Extension points
With this new design there is an option to write custom RDBMS or any DBMS specific store and plug it to MB. For instance you can write custom classes implementing AndesContextStore and MessageStore interfaces to harness performance gaines by using specific SQL statements supported by a given database.
Written by Asitha Nanayakkara